MPLS Study Notes Terminology
Multiprotcol
Transport diff payloads
-Ethernet, FRLY, ATM,IPv4, IPv6
Layer 3 MPLS VPN (RFC2547) will be the focus of the 4.0 R&S Exam.
Label Switching
- Labels used to route(switch)traffic instead of normal IPv4/IPv5 route.
- Similar to how FRLY DLCI or ATM VPI/VCI works….
- Labels are locally significant between each adjacent neighbor.
- MPLS TE(Traffic Engineering), fast convergence…
- SP no longer has to hold 300k routes on every router in their network.
How MPLS Works
- Layer2 or Layer3 traffic enters SP network.
- MPLS label is added to incoming traffic at SP edge(PE) or (LSR).
- SP core switches traffic towards exit point using MPLS label
- MPLS label is removed as traffic exits SP network
- Traffic is “tunneled” from SP entry to SP exit since SP core does not inspect payload.
How Labels Work
Each label represents a unique IP prefix
- Label to IP binding is called a Forwarding Equivalence Class(FEC)
Labels are dynamically advertised using a Label Distribution Protocol. LDP and TDP use IS-IS or OSPF.
- Tag Distribution Protocol(TDP)
- >> Legacy and Cisco Proprietary
- Label Distribution Protocol(LDP)…Most common(TCP based)
- >> Open Standard
- BGP
- >> Multiprotocol Extensions…MP-BGP or MBGP
- Resource Reservation Protocol(RSVP)
- >> Used for MPLS TE
We are going to look at LDP and BGP for the 4.0 Exam.
How Switching Works
Label + Prefix binding forms Label Forwarding Information Base (LFIB)
When traffic is received, LFIB is consulted in order to perform one of 3 operations
- Label push(ADD)
Add a label to an incoming packet
AKA label imposition
- Label swap(Change)
Replace the label on an incoming packet
- Label pop(Remove)
Remove the label from an outgoing packet
AKA label disposition
MPLS Terms
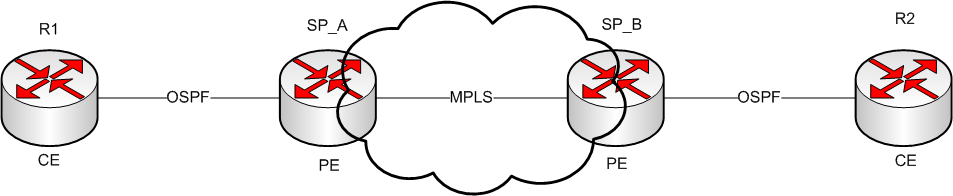
Customer Edge (CE) Router
- CPE equip that typically does not run MPLS
- Can be layer 2 only or layer 3 aware
Provider Edge (PE) Router
- Receives traffic from Customer Edge(CE) devices, adds MPLS label(push), and forwards into core
- Receives traffic from core, removes MPLS labels(pop), and forwards towards Customer Edge(CE) devices.
Provider (P) Router
- Connects only to PE’s and other P routers
- Switches traffic between interfaces based on MPLS labels(swap)
